| Title |
LeBlanc, Crystal MED_2024 |
| Alternative Title |
Spelling Curriculum Based On LETRS Principles |
| Creator |
LeBlanc, Crystal |
| Collection Name |
Master of Education |
| Description |
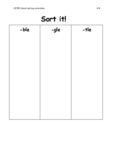
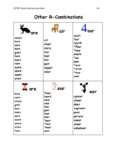
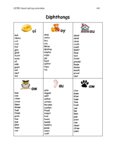
This paper illuminates the essential components required for implementing a successful spelling program using the teaching of phonological awareness, phonics, morphology, etymology, and spelling rules. |
| Abstract |
Student spelling proficiency relies on teachers' linguistic knowledge, research-based spelling curriculum, and explicit instruction. Historically, spelling instruction has often relied heavily on rote memorization strategies. Traditional approaches typically involved students memorizing lists of words, practicing spelling drills, and being tested on their ability to recall and reproduce correct spellings. Memorization alone does not necessarily foster a deep understanding of language structure or orthographic principles and does not give the students the foundational linguistic tools needed for more complex tasks. Recognizing these shortcomings through research, professional development and curriculum emphasize not only memorization but also the teaching of phonological awareness, phonics, morphology, etymology, and spelling rules. These approaches aim to deepen students' understanding of language structure and enhance their ability to analyze and manipulate words. This paper illuminates the essential components required for implementing a successful spelling program. |
| Subject |
Education, Elementary; Educational evaluation; Language and languages--Study and teaching |
| Digital Publisher |
Stewart Library, Weber State University, Ogden, Utah, United States of America |
| Date |
2024 |
| Medium |
theses |
| Type |
Text |
| Access Extent |
144 MB; 489 page pdf |
| Rights |
The author has granted Weber State University Archives a limited, non-exclusive, royalty-free license to reproduce his or her theses, in whole or in part, in electronic or paper form and to make it available to the general public at no charge. The author retains all other rights. |
| Source |
University Archives Electronic Records: Master of Education. Stewart Library, Weber State University |
| Format |
application/pdf |
| ARK |
ark:/87278/s6k3xd8f |
| Setname |
wsu_smt |
| ID |
129215 |
| Reference URL |
https://digital.weber.edu/ark:/87278/s6k3xd8f |