| Title |
1850 - 2000 History of Marriott-Slaterville City Volume 1 |
| Creator |
Marriott-Slaterville City |
| Contributors |
Marriott-Slaterville City and its Residents |
| Description |
The Marriott-Slaterville City History Collection was created by the residents of the town to document their history. The collection includes Autobiographies, Oral Histories, History of Marriott, History of Slaterville, and the History of the Merging Townships to create Marriott-Slaterville City. This information has left behind rich histories, stories and important information regarding the history of the Marriott-Slaterville area. |
| Subject |
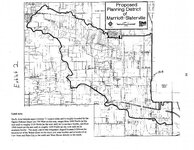
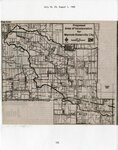
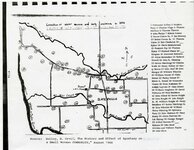
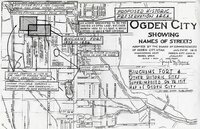
Marriott-Slaterville (Utah); Ogden (Utah) |
| Digital Publisher |
Stewart Library, Weber State University, Ogden, Utah, USA |
| Date Original |
2000 |
| Date |
2000 |
| Date Digital |
2014 |
| Temporal Coverage |
1850; 1851; 1852; 1853; 1854; 1855; 1856; 1857; 1858; 1859; 1860; 1861; 1862; 1863; 1864; 1865; 1866; 1867; 1868; 1869; 1870; 1871; 1872; 1873; 1874; 1875; 1876; 1877; 1878; 1879; 1880; 1881; 1882; 1883; 1884; 1885; 1886; 1887; 1888; 1889; 1890; 1891; 1892; 1893; 1894; 1895; 1896; 1897; 1898; 1899; 1900; 1901; 1902; 1903; 1904; 1905; 1906; 1907; 1908; 1909; 1910; 1911; 1912; 1913; 1914; 1915; 1916; 1917; 1918; 1919; 1920; 1921; 1922; 1923; 1924; 1925; 1926; 1927; 1928; 1929; 1930; 1931; 1932; 1933; 1934; 1935; 1936; 1937; 1938; 1939; 1940; 1941; 1942; 1943; 1944; 1945; 1946; 1947; 1948; 1949; 1950; 1951; 1952; 1953; 1954; 1955; 1956; 1957; 1958; 1959; 1960; 1961; 1962; 1963; 1964; 1965; 1966; 1967; 1968; 1969; 1970; 1971; 1972; 1973; 1974; 1975; 1976; 1977; 1978; 1979; 1980; 1981; 1982; 1983; 1984; 1985; 1986; 1987; 1988; 1989; 1990; 1991; 1992; 1993; 1994; 1995; 1996; 1997; 1998; 1999; 2000 |
| Medium |
histories |
| Spatial Coverage |
Marriott-Slaterville (Utah); Weber County (Utah) |
| Type |
Text |
| Conversion Specifications |
Archived TIFF images were scanned with an Epson Expression 10000XL scanner. |
| Language |
eng |
| Relation |
https://archivesspace.weber.edu/repositories/3/resources/506 |
| Rights |
Materials may be used for non-profit and educational purposes; please credit the Special Collections Department, Stewart Library, Weber State University. |
| Source |
MS 351 Special Collections, Stewart Library, Weber State University |
| Format |
application/pdf |
| ARK |
ark:/87278/s67cba7k |
| Setname |
wsu_ms |
| ID |
60832 |
| Reference URL |
https://digital.weber.edu/ark:/87278/s67cba7k |
| Title |
167_page149 |
| Creator |
Marriott-Slaterville City |
| Contributors |
Marriott-Slaterville City and its Residents |
| Description |
The Marriott-Slaterville City History Collection was created by the residents of the town to document their history. The collection includes Autobiographies, Oral Histories, History of Marriott, History of Slaterville, and the History of the Merging Townships to create Marriott-Slaterville City. This information has left behind rich histories, stories and important information regarding the history of the Marriott-Slaterville area. |
| Subject |
Marriott-Slaterville (Utah); Ogden (Utah) |
| Digital Publisher |
Stewart Library, Weber State University |
| Date Original |
2000 |
| Date |
2000 |
| Date Digital |
2014 |
| Type |
Text |
| Conversion Specifications |
Archived TIFF images were scanned at 400 dpi with an Epson Expression 10000XL scanner. |
| Language |
eng |
| Relation |
http://library.weber.edu/asc/speccoll/AlphaListing.cfm#I |
| Rights |
Materials may be used for non-profit and educational purposes; please credit the Special Collections Department, Stewart Library, Weber State University. |
| Source |
MS 351 Special Collections, Stewart Library, Weber State University |
| Format |
application/pdf |
| Setname |
wsu_ms |
| ID |
62018 |
| Reference URL |
https://digital.weber.edu/ark:/87278/s67cba7k/62018 |